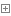
通过class.getMethos()方法获得类的所有公共方法包括父类的公共方法。
1 import lombok.Data; 2 3 /** 4 * Created by hunt on 2017/6/27. 5 * 测试的实体类 6 * @Data 编译后会自动生成set、get、无惨构造、equals、canEqual、hashCode、toString方法 7 */ 8 @Data 9 public class Person { 10 private String name; 11 public String nickName; 12 private int age; 13 private void say(){ 14 System.out.println("say hunt"); 15 } 16 }
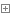
1 import java.lang.reflect.Method; 2 3 /** 4 * Created by hunt on 2017/6/27. 5 */ 6 public class NewInstanceTest { 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 Class<Person> personClass = Person.class; 9 try { 10 Method[] methods = personClass.getMethods(); 11 for (Method m:methods) { 12 System.out.println(m); 13 } 14 } catch (Exception e) { 15 e.printStackTrace(); 16 } 17 } 18 }
通过class.getDeclaredMethods()方法获得类的所有属性(公共,保护,默认,和私有方法)。
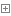
1 import java.lang.reflect.Method; 2 3 /** 4 * Created by hunt on 2017/6/27. 5 */ 6 public class NewInstanceTest { 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 Class<Person> personClass = Person.class; 9 try { 10 Method[] methods = personClass.getDeclaredMethods(); 11 for (Method m:methods) { 12 System.out.println(m); 13 } 14 } catch (Exception e) { 15 e.printStackTrace(); 16 } 17 } 18 }
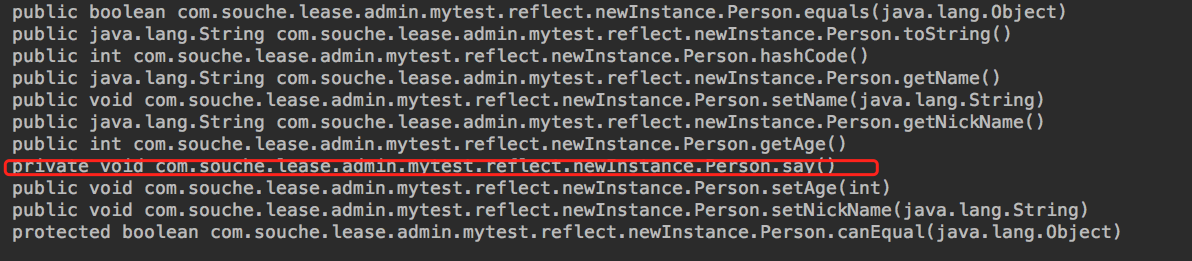
注意:返回的方法数组中的元素没有排序,也没有任何特定的顺序。
获得具体的方法:
1 import java.lang.reflect.Method; 2 3 /** 4 * Created by hunt on 2017/6/27. 5 */ 6 public class NewInstanceTest { 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 Class<Person> personClass = Person.class; 9 try { 10 Person p = personClass.newInstance(); 11 Method method = personClass.getMethod("setName", String.class); 12 method.invoke(p,"hunt"); 13 System.out.println(p); 14 method = personClass.getMethod("getName"); 15 System.out.println("getName方法"+method.invoke(p)); 16 method = personClass.getDeclaredMethod("say"); 17 method.setAccessible(true);//私有方法要授权 18 method.invoke(p); 19 } catch (Exception e) { 20 e.printStackTrace(); 21 } 22 } 23 }
总结:personClass.getDeclaredMethod("say");
method.setAccessible(true);
基于对属性的保护,默认为false。这里相当于一个授权的过程,设置true来允许操作这个属性。