HashMap 的一些认识: (JDK 1.7)
- 基于哈希表的Map接口的非同步实现,定义了键映射到值的规则
- 此实现提供所有可选的映射操作,并允许使用null值和null键
- 此实现假定哈希函数将元素适当分布在各桶之间,为读取操作提供稳定性能
- 迭代时间与实例容量(桶的数量)及其大小(键-值映射关系数)成正比
■ 类定义
public class HashMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V> implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable
- 继承 AbstractMap抽象类,实现了Map接口
- 实现 Cloneable接口
- 实现 java.io.Serializable 接口,支持序列化
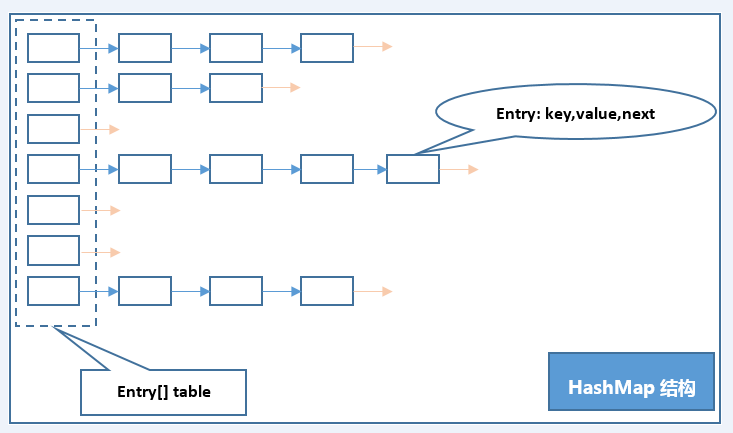
HashMap - “链表散列” (数组+链表), 数组每一项都是一条链的数据结构
//The default initial capacity - MUST be a power of two. static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16; //The maximum capacity - MUST be a power of two <= 1<<30. static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30; //The load factor used when none specified in constructor. static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f; //The table, resized as necessary. Length MUST Always be a power of two. transient Entry<K,V>[] table; //The number of key-value mappings contained in this map. transient int size; //The next size value at which to resize (capacity * load factor). int threshold; //The load factor for the hash table. final float loadFactor; /** * The number of times this HashMap has been structurally modified * Structural modifications are those that change the number of mappings in * the HashMap or otherwise modify its internal structure (e.g., * rehash). This field is used to make iterators on Collection-views of * the HashMap fail-fast. (See ConcurrentModificationException). */ transient int modCount;
■ 构造器
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) { if (initialCapacity < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " + initialCapacity); if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY; if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " + loadFactor); // Find a power of 2 >= initialCapacity int capacity = 1; while (capacity < initialCapacity) capacity <<= 1; this.loadFactor = loadFactor; //阈值为容量*负载因子和最大容量+1之间的最小值 以此值作为容量翻倍的依据(不能超过最大容量) threshold = (int)Math.min(capacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1); //初始化一个2次幂的Entry类型数组 一个桶对应一个Entry对象 table = new Entry[capacity]; useAltHashing = sun.misc.VM.isBooted() && (capacity >= Holder.ALTERNATIVE_HASHING_THRESHOLD); init(); }
- Entry
/** * 静态类 默认实现内部Entry接口 (接口中可定义内部接口-Map.Entry接口为Map的内部接口) * PS:JDK8中引入default,作用为在接口中定义默认方法实现 */ static class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { final K key;//key具有引用不可变特性 V value; Entry<K,V> next;//next指向下一个:单向链表,头插入 final int hash; …… }
■ 主要方法
put(k, v)
/** * @return key不存在返回null,否则返回旧值 */ public V put(K key, V value) { //其允许存放null的key和null的value //当其key为null时,调用putForNullKey方法,放入到table[0]的这个位置(null键只有一个) if (key == null) return putForNullKey(value); //通过调用hash方法对key进行哈希,得到哈希之后的数值 //其目的是为了尽可能的让键值对可以分不到不同的桶中 int hash = hash(key); //根据上一步骤中求出的hash得到在数组中是索引i int i = indexFor(hash, table.length); //如果i处的Entry不为null,则通过其next指针不断遍历e元素的下一个元素。 for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) { Object k;//使用临时变量k主要用于e.key的赋值,意义有限 //hash一致 && (key引用相同 或 key字符串比较相同) if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) { //值变更 V oldValue = e.value; e.value = value; e.recordAccess(this); return oldValue;//已存在则选择直接返回旧值 } } modCount++; addEntry(hash, key, value, i);//新增 return null;//若key不存在则返回null }
hash()
//JDK1.7 final int hash(Object k) { int h = 0; if (useAltHashing) { if (k instanceof String) { return sun.misc.Hashing.stringHash32((String) k); } h = hashSeed; } //异或就是两个数的二进制形式,按位对比,相同取0,不同取一 //此算法加入了高位计算,防止低位不变,高位变化时,造成的 hash 冲突 h ^= k.hashCode(); h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12); return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4); } //JDK1.8 扰动函数 -> 散列值优化函数 static final int hash(Object key) { int h; //把一个数右移16位即丢弃低16为,就是任何小于2^16的数,右移16后结果都为0 //2的16次方再右移刚好就是1 同时int最大值为32位 //任何一个数,与0按位异或的结果都是这个数本身 //为indexFor做准备 return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16); }
indexFor()
/** * Int范围(2^32)从-2147483648到2147483648,加起来大概40亿空间,内存不能直接读取 * 用之前还要先做对数组的长度取模运算,得到的余数才能用来访问数组下标 * @Param h 根据hash方法得到h * @Param length 一定是2次幂 */ static int indexFor(int h, int length) { //2次幂-1 返回的结果的二进制为永远是都是1 比如 15 -> 1111 (16 -> 10000) //与运算 只有 1 & 1 = 1 正好相当于一个“低位掩码” //如果length-1中某一位为0,则不论h中对应位的数字为几,对应位结果都是0,这样就让两个h取到同一个结果,hash冲突 //同时这个操作可以保证索引不会大于数组的大小(见开头的描述) return h & (length-1); }
addEntry()
//该方法为包访问 package java.util(本包私有性高于子类) void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) { //当前容量超过阈值 && 当前坐标数组非空 //有个优雅的设计在于,若bucketIndex处没有Entry对象,那么新添加的entry对象指向null,从而就不会有链了 if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) { resize(2 * table.length);//容量扩容一倍 hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0;//hash重新计算 bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length);//index重新计算 } createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);//新增Entry元素到数组的制定下标位置 } //该方法为包访问 package java.util void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) { // 获取指定 bucketIndex 索引处的 Entry Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex]; // 将新创建的 Entry 放入 bucketIndex 索引处,并让新的 Entry 指向原来的 Entry // 形成链表,新加入的放入链表头部,最先加入的放入尾部 table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e); size++; }
remove()
public V remove(Object key) { Entry<K,V> e = removeEntryForKey(key); return (e == null ? null : e.value); } /** * Removes and returns the entry associated with the specified key * in the HashMap. Returns null if the HashMap contains no mapping * for this key. */ final Entry<K,V> removeEntryForKey(Object key) { int hash = (key == null) ? 0 : hash(key); int i = indexFor(hash, table.length); Entry<K,V> prev = table[i];//用于记录该key的前一个元素(默认先从队首开始) Entry<K,V> e = prev;//从队首开始往队尾遍历 //遍历key所在链表 while (e != null) { Entry<K,V> next = e.next; Object k; if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) { modCount++;//remove属于结构性改造,modCount计数+1 size--;//当前Map的有效元素数量-1 if (prev == e) table[i] = next;//若当前key正好位于队首,则队首指向next else prev.next = next;//若当前key不位于队首,则该key之前的元素的next指向该key的下一个元素 e.recordRemoval(this);//LinkedHashMap专用方法 return e; } //继续往队尾找 prev = e;//指向当前循环元素的上一个元素 e = next;//指向下一次循环元素 } return e; }
■ HashMap 迭代
//方法一 Iterator<Map.Entry<Integer,Object>> it = map.entrySet().iterator(); while (it.hasNext()) { Map.Entry<Integer, Object> entry = it.next(); System.out.println("key=" + entry.getKey() + " and value=" + entry.getValue());
//在迭代中可删除 Map 元素也是推荐,避免快速失败 }
//方法二 for (Map.Entry<Integer,Object> entry : map.entrySet()) { System.out.println("key=" + entry.getKey() + " and value=" + entry.getValue()); }
***** 此版本为JDK 1.7,由于笔者水平有限,之后有补充的话会更新此文,请各位看客多多谅解支持 ********
***** JDK1.8 的 HashMap 之后会另写一篇 ******