一 @PostConstruct介绍
从Java
EE5规范开始,Servlet增加了两个影响Servlet生命周期的注解(Annotation):@PostConstruct和@PreConstruct。这两个注解被用来修饰一个非静态的void()方法.而且这个方法不能有抛出异常声明。
@PostContruct是spring框架的注解,在方法上加该注解会在项目启动的时候执行该方法,也可以理解为在spring容器初始化的时候执行该方法。
写法有如下两种方式:
@PostConstruct //方式1 public void someMethod(){ ... } public @PostConstruct void someMethod(){ //方式2 ... }
被@PostConstruct修饰的方法会在服务器加载Servle的时候运行,并且只会被服务器执行一次。PostConstruct在构造函数之后执行,init()方法之前执行。PreDestroy()方法在destroy()方法执行执行之后执行
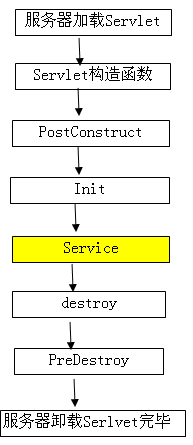
二 @PostConstruct在项目中的用处
1.spring项目加载数据字典
@PostConstruct注解的方法在项目启动的时候执行这个方法,也可以理解为在spring容器启动的时候执行,可作为一些数据的常规化加载,比如数据字典之类的。
2.spring项目的定时任务
spring自带的@schedule,没有开关,项目启动总会启动一个线程;
做项目的时候就使用Java的timer,这个设置开关即可自由的控制,关闭的时候,不会启动线程;
Java的timer也需要找到一个启动类,可以放到main函数里面启动,这样的话,代码的耦合性太高了,而使用PostConstruct是很干净的。
3 servlet初始化加载之前处理像加载缓存等。
用的不多,因为如果初始化之前我们要加载或处理某些玩意完全可以在构造器初始化时就处理了,但这种方法需要自己重写构造器。
1 package com.whaty.products.whatysns.web.info; 2 3 import javax.annotation.PostConstruct; 4 import javax.annotation.Resource; 5 6 import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; 7 import org.springframework.util.Assert; 8 9 import com.whaty.framework.cache.core.model.Cache; 10 import com.whaty.framework.cache.core.service.CacheService; 11 import com.whaty.framework.cache.entitycache.service.EntityCacheHelper; 12 import com.whaty.framework.cache.entitycache.service.IEntityDaoAdapter; 13 14 /** 15 * @author 16 * @param <KEY> 17 * @param <ENTITY> 18 */ 19 @Service("AjaxCacheableService") 20 public class AjaxCacheableService{ 21 22 @Resource(name="cacheService") 23 protected CacheService cacheService; 24 25 protected boolean useReadWriteEntityDao = false; 26 protected boolean useCache = true; 27 protected int entityCacheMaxSize = 1000; 28 protected int entityCacheMaxLiveSeconds = 3600; 29 protected Cache entityCache; 30 31 32 /** 33 * 构造方法执行后,初始化, 34 */ 35 @PostConstruct 36 public void init() { 37 Assert.notNull(cacheService, "cacheService must be set!"); 38 getCache(); 39 } 40 41 /** 42 * 获取cache 43 * @return 44 */ 45 protected Cache getCache() { 46 if (entityCache == null) { 47 entityCache = cacheService.addCache(this.getClass().getName(),entityCacheMaxLiveSeconds); 48 } 49 return entityCache; 50 } 51 52 /** 53 * @param id 54 * @param useCache 是否使用Cache 55 * @return 56 */ 57 public Object getCache(String id) { 58 String strid = String.valueOf(id); 59 Object o = entityCache.get(strid); 60 return o; 61 } 62 63 public Object putCache(int tTLSeconds,String cacheId,Object value) { 64 String strid = String.valueOf(cacheId); 65 Object o = entityCache.get(strid); 66 if (o != null) { 67 return o; 68 } else { 69 entityCache.put(strid, value, tTLSeconds); 70 return value; 71 } 72 } 73 74 }
三 工程
1 <!-- @PostConstruct和@PreDestroy注解 --> 2 <servlet> 3 <servlet-name>AnnotationServlet</servlet-name> 4 <servlet-class>com.servlet.AnnotationServlet</servlet-class> 5 </servlet> 6 <servlet-mapping> 7 <servlet-name>AnnotationServlet</servlet-name> 8 <url-pattern>/servlet/AnnotationServlet</url-pattern> 9 </servlet-mapping>
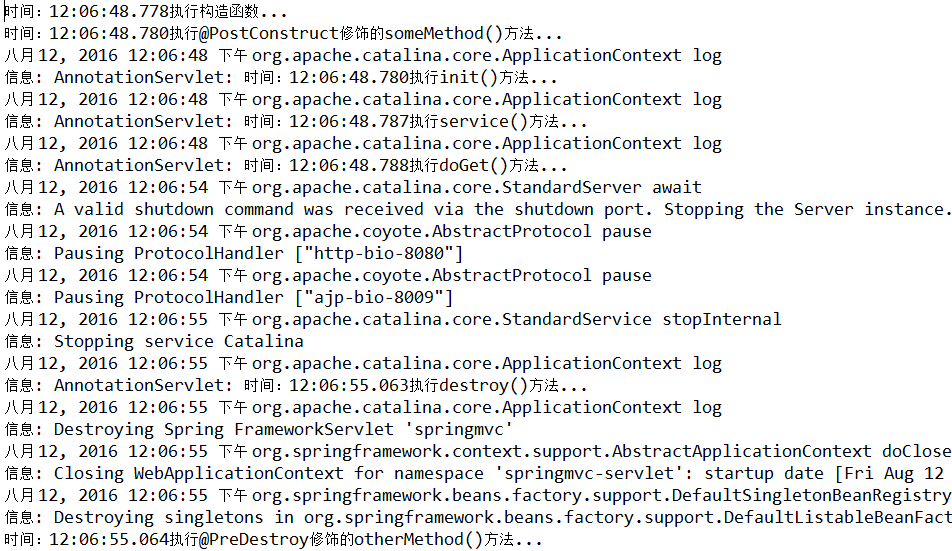
1 package com.servlet; 2 3 import java.io.IOException; 4 import java.io.PrintWriter; 5 import java.sql.Time; 6 import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; 7 import java.util.Date; 8 9 import javax.annotation.PostConstruct; 10 import javax.annotation.PreDestroy; 11 import javax.servlet.ServletException; 12 import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; 13 import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; 14 import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; 15 16 public class AnnotationServlet extends HttpServlet { 17 SimpleDateFormat df = new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss.SSS");//设置日期格式,精确到毫秒 18 19 public AnnotationServlet(){ 20 System.out.println("时间:"+df.format(new Date())+"执行构造函数..."); 21 } 22 23 public void destroy() { 24 this.log("时间:"+df.format(new Date())+"执行destroy()方法..."); 25 //super.destroy(); // Just puts "destroy" string in log 26 // Put your code here 27 } 28 29 @PostConstruct 30 public void someMethod(){ 31 //this.log("执行@PostConstruct修饰的someMethod()方法...");//注意:这样会出错 32 System.out.println("时间:"+df.format(new Date())+"执行@PostConstruct修饰的someMethod()方法..."); 33 } 34 35 @PreDestroy 36 public void otherMethod(){ 37 System.out.println("时间:"+df.format(new Date())+"执行@PreDestroy修饰的otherMethod()方法..."); 38 } 39 40 public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) 41 throws ServletException, IOException { 42 this.log("时间:"+df.format(new Date())+"执行doGet()方法..."); 43 } 44 45 public void init() throws ServletException { 46 // Put your code here 47 this.log("时间:"+df.format(new Date())+"执行init()方法..."); 48 } 49 50 protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) 51 throws ServletException, IOException{ 52 this.log("时间:"+df.format(new Date())+"执行service()方法..."); 53 super.service(request, response); 54 } 55 56 }
四 spring中Constructor、@Autowired、@PostConstruct的顺序
Constructor >> @Autowired >> @PostConstruct
要将对象p注入到对象a,那么首先就必须得生成对象p与对象a,才能执行注入。
所以,如果一个类A中有个成员变量p被@Autowired注解,那么@Autowired注入是发生在A的构造方法执行完之后的。
如果想在生成对象时候完成某些初始化操作,而偏偏这些初始化操作又依赖于依赖注入,那么就无法在构造函数中实现。
为此,可以使用@PostConstruct注解一个方法来完成初始化,@PostConstruct注解的方法将会在依赖注入完成后被自动调用。