1.异常
1.0 异常的概念

2.throw关键字

public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int []arc=null;
getelem(arc,0);
}
private static int getelem(int arc[],int index) {
if(arc==null){
throw new NullPointerException("空指针异常!");
}
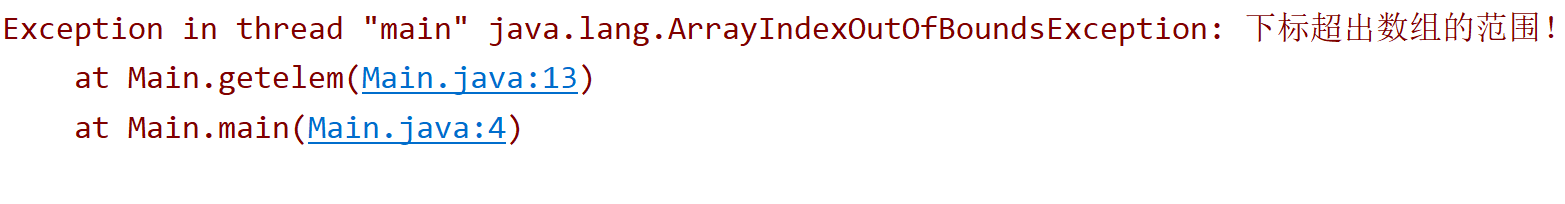
return arc[index];
}
}

public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int []arc=new int[3];
getelem(arc,3);
}
private static int getelem(int arc[],int index) {
if(arc==null){
throw new NullPointerException("空指针异常!");
}
else if(index>=arc.length||index<0)
{
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("下标超出数组的范围!");
}
return arc[index];
}
}
3.Objects 非空判断
import java.util.Objects;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arc[]=null;
Objects.requireNonNull(arc,"空指针异常");
}
}
4.异常处理的第一种方法 throws关键字

import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.module.FindException;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//判断路径是否是C:\\.txt
Filename("C:\\.tx");
}
private static void Filename(String s) throws Exception {
//FileNotFoundException extends IOException extends Exception
if(!s.equals("C:\\.txt")){
throw new FileNotFoundException("该路径不是C:\\.txt");
}
if(!s.endsWith(".txt"))
throw new IOException("文件后缀不是.txt");
}
}
5.异常处理的第二种方法
try...catch()

import java.lang.invoke.MethodHandles;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arc=new int[3];
try {
int getelem = getelem(arc, 3);
}catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e)
{
System.out.println("程序由catch处理");
}
System.out.println("后续代码");
//如果抛出throws 程序交给JVM处理 程序遇到异常就会中断
}
private static int getelem(int arc[],int index) throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException{
if(index<0||index>=arc.length)
{
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("下标超出数组的长度范围");
}
return arc[index];
}
}
打印结果:
程序由catch处理
后续代码
6.Throwable类中常用的方法

import java.lang.invoke.MethodHandles;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arc=new int[3];
try {
int getelem = getelem(arc, 3);
}catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e)
{
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
System.out.println(e.toString());
System.out.println(e);
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("后续代码");
//如果抛出throws 程序交给JVM处理 程序遇到异常就会中断
}
private static int getelem(int arc[],int index) throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException{
if(index<0||index>=arc.length)
{
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("下标超出数组的长度范围");
}
return arc[index];
}
}
打印结果:
下标超出数组的长度范围
java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 下标超出数组的长度范围
java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 下标超出数组的长度范围
后续代码
java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 下标超出数组的长度范围
at Main.getelem(Main.java:24)
at Main.main(Main.java:7)
7.异常处理的注意事项
(1)多个异常对象
import java.util.List;
/*
* 异常处理:多个异常对象的处理
* 1、多个异常分别处理
* 2、多个异常一次捕获,多次处理
* 3、多个异常一次捕获一次处理
* */
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//int []arc=new int[3];
//System.out.println(arc[3]);//ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException 3
//List<Integer> list = List.of(4, 3, 26, 6);
//System.out.println(list.get(4));//IndexOutOfBoundsException
/*1.多个异常分别处理
try{
int []arc=new int[3];
System.out.println(arc[3]);
}catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e)
{
System.out.println(e);
}
try{
List<Integer> list = List.of(4, 3, 26, 6);
System.out.println(list.get(4));
}catch(IndexOutOfBoundsException e)
{
System.out.println(e);
}
java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 3
java.lang.IndexOutOfBoundsException: Index 4 out-of-bounds for length 4
*/
/*
2.多个异常一次捕获多次处理
注意事项 子类对象必须写在父类对象之上
try{
int []arc=new int[3];
System.out.println(arc[3]);
List<Integer> list = List.of(4, 3, 26, 6);
System.out.println(list.get(4));
}
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){
System.out.println(e);
}
catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e)
{
System.out.println(e);
}
}
*/
/*
3、多个异常一次捕获一次处理
try{
int []arc=new int[3];
System.out.println(arc[3]);
List<Integer> list = List.of(4, 3, 26, 6);
System.out.println(list.get(4));
}
catch(Exception e)
{
System.out.println(e);
}
}
*/
}
}
(2)finally代码块里有return语句
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int method = method();
System.out.println(method);//20
}
private static int method() {
try{
int a[]=null;
int sum=0;
return sum;
}catch(NullPointerException e)
{
System.out.println(e);
}
finally {
int sum=20;
return sum;
}
}
}
(3)子父类异常

public class FU {
public void show1() throws NullPointerException, ClassCastException { }
public void show2() throws IndexOutOfBoundsException { };
public void show3() throws IndexOutOfBoundsException { };
public void show4() { }
}
class ZI extends FU{
@Override
public void show1() throws NullPointerException, ClassCastException { }
public void show2() throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException{}
@Override
public void show3(){}
public void show4(){
try {
throw new Exception("编译器异常");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
(4)自定义异常类


public class ReadException extends Exception{
public ReadException() {
}
public ReadException(String message) {//添加一个带异常信息的构造方法
super(message);
}
}
(5)自定义异常的小练习
注册名称
public class RegisterException extends Exception {
public RegisterException(String message) {
super(message);
}
public RegisterException() {
}
}
1)通过throws方法处理异常
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Register {
public static String []name={"Mary","Lisa","Jennie","JK","Minnie"};//全局变量
public static void main(String[] args) throws RegisterException {
System.out.println("请输入您要注册的姓名:");
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
String usename=input.next();
Checkname(usename);
}
public static void Checkname(String usename) throws RegisterException {
for (String s : name) {
if(s.equals(usename))//true
{
throw new RegisterException("对不起,您的名字已经被注册过!");
}
}
System.out.println("恭喜您,注册成功!");
}
}
请输入您要注册的姓名:
jhfshdbfbsfhe
恭喜您,注册成功!
请输入您要注册的姓名:
Mary
Exception in thread "main" RegisterException: 对不起,您的名字已经被注册过!
at Register.Checkname(Register.java:16)
at Register.main(Register.java:9)
2)try...catch()处理
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Register {
public static String []name={"Mary","Lisa","Jennie","JK","Minnie"};//全局变量
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("请输入您要注册的姓名:");
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
String usename=input.next();
Checkname(usename);
}
public static void Checkname(String usename){
for (String s : name) {
if(s.equals(usename))//true
{
try {
throw new RegisterException("对不起,您的名字已经被注册过!");
} catch (RegisterException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return;
}
}
}
System.out.println("恭喜您,注册成功!");
}
}
3)也可以将RegisterException 继承RuntimeException
public class RegisterException extends RuntimeException {
public RegisterException(String message) {
super(message);
}
public RegisterException() {
}
}
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Register {
public static String []name={"Mary","Lisa","Jennie","JK","Minnie"};//全局变量
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("请输入您要注册的姓名:");
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
String usename=input.next();
Checkname(usename);
}
public static void Checkname(String usename){
for (String s : name) {
if(s.equals(usename))//true
{
throw new RegisterException("对不起,您的名字已经被注册过!");
}
}
System.out.println("恭喜您,注册成功!");
}
}
2.线程
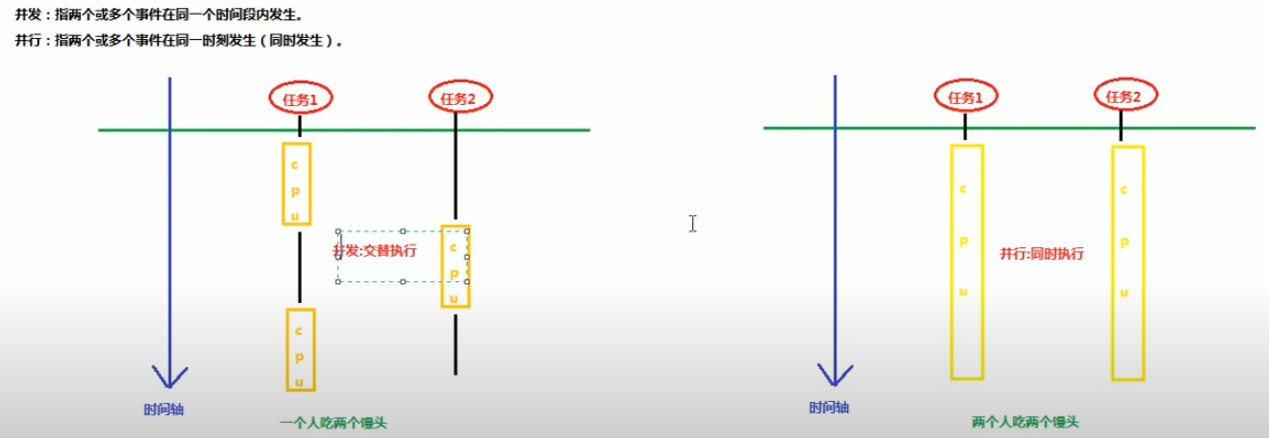
1.0 并发和并行
2.进程与线程

线程的概念以及对线程的分析
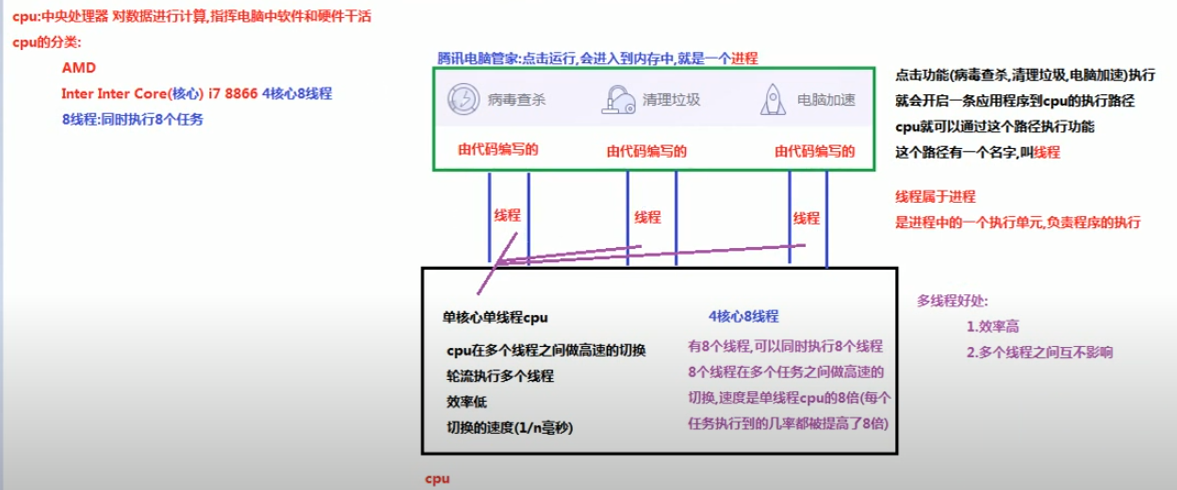
3.线程的调度

4.主线程

5.创建多线程程序
第一种创建方式

public class Mythread extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
{
System.out.println("run:"+i);
}
}
}
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Mythread mt=new Mythread();
mt.start();
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
{
System.out.println("Main:"+i);
}
}
}
第一次打印结果:
Main:0
Main:1
run:0
Main:2
Main:3
run:1
Main:4
run:2
run:3
run:4
第二次打印结果:
Main:0
run:0
Main:1
run:1
Main:2
run:2
Main:3
run:3
Main:4
run:4
每次打印结果可能不同 因为多个线程并发 抢占式调度
两个线程 一个main线程 一个新线程 抢夺CPU(执行时间)
第二种方式

public class RunnableImpl implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"--->"+i);
}
}
}
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
RunnableImpl impl=new RunnableImpl();
Thread t=new Thread(impl);
t.start();
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"--->"+i);
}
}
}
打印结果:
main--->0
main--->1
Thread-0--->0
main--->2
Thread-0--->1
Thread-0--->2
main--->3
Thread-0--->3
main--->4
Thread-0--->4
实现Runnable接口创建多线程程序的好处

6.Thread类常用方法
(1)获取线程名称

(2) 设置线程的名称

public class Mythread extends Thread {
public Mythread(String name) {
super(name);
}
public Mythread() {
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Mythread mt=new Mythread();
mt.setName("START");//START
mt.start();
new Mythread("Hello").start();//Hello
}
}
(3)sleep方法

一秒打印一个数
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 1; i <=10 ; i++) {
System.out.println(i);
try{
Thread.sleep(1000);
}catch(InterruptedException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
7.匿名内部类方式实现线程的创建

public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*第一种创建方式
new Thread(){
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i=1;i<=5;i++)
{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"->"+i);
}
}
}.start();
*/
/*第二种通过Runnable接口
(1)
Runnable r=new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i=1;i<=5;i++)
{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"->"+i);
}
}
};
new Thread(r).start();
(2)简化版本
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i=1;i<=5;i++)
{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"->"+i);
}
}
}).start();
*/
for(int i=1;i<=5;i++)
{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"->"+i);
}
}
}
3.线程安全问题
1.0 概述
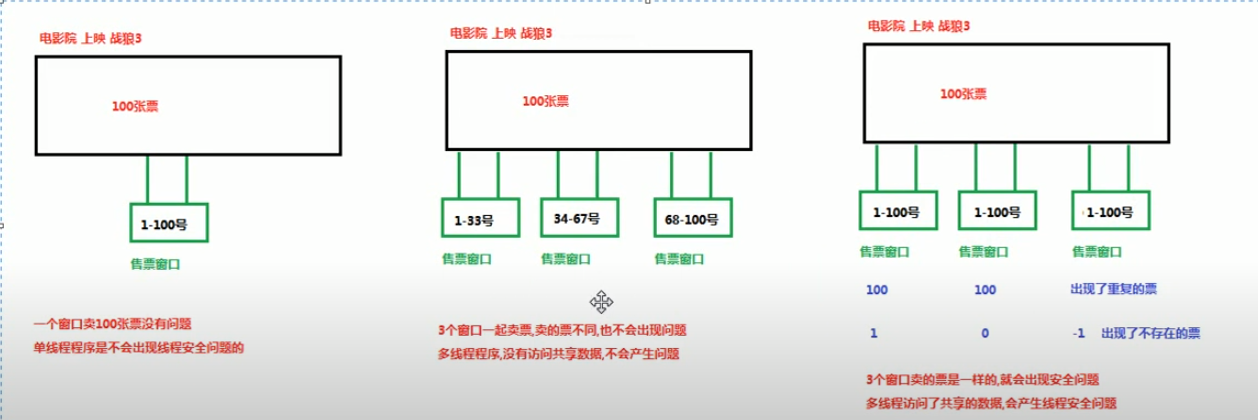
2.线程安全问题产生
public class RunnableImpl implements Runnable{
private int ticket=100;
@Override
public void run() {
while(true)
{
if(ticket>0)
{
try{
Thread.sleep(100);
}catch(Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"正在售出第"+ticket+"张票");
ticket--;
}
}
}
}
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
RunnableImpl r=new RunnableImpl();
Thread r1=new Thread(r);
Thread r2=new Thread(r);
Thread r3=new Thread(r);
r1.start();
r2.start();
r3.start();
}
}

结果中出现 1 0 -1 不存在的票说明 在共享数据的同时发生了安全性问题
3.解决线程安全问题
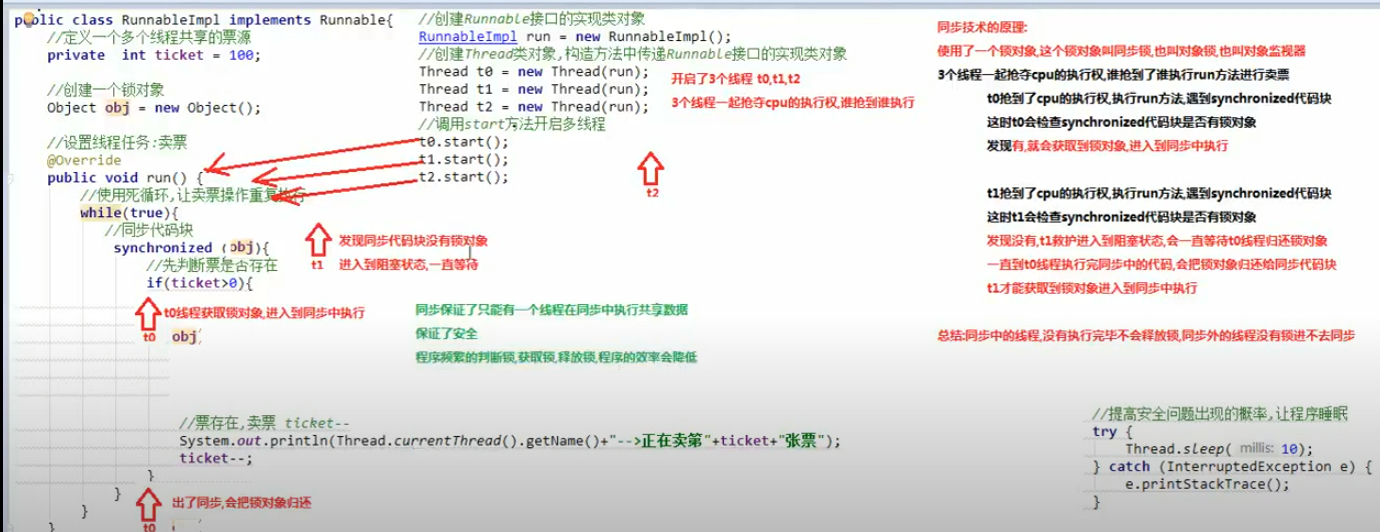
(1)第一种方式 同步代码块

public class RunnableImpl implements Runnable{
private int ticket=100;
Object obj=new Object() ;
@Override
public void run() {
while(true)
{
synchronized (obj)
{
if(ticket>0)
{
try{
Thread.sleep(100);
}catch(Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"正在售出第"+ticket+"张票");
ticket--;
}
}
}
}
}
同步技术的原理
(2)第二种方法 同步方法


public class RunnableImpl implements Runnable{
private int ticket=100;
@Override
public void run() {
while(true)
{
payticket();
}
}
public synchronized void payticket()
{
if(ticket>0)
{
try{
Thread.sleep(100);
}catch(Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"正在售出第"+ticket+"张票");
ticket--;
}
}
}
------静态同步方法

(3)第三种方式 Lock锁

写法一:
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
public class RunnableImpl implements Runnable{
private int ticket=100;
Lock l=new ReentrantLock();
@Override
public void run() {
while (true)
{
l.lock();
if(ticket>0)
{
try{
Thread.sleep(100);
}catch(Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"正在售出第"+ticket+"张票");
ticket--;
}
l.unlock();
}
}
}
写法二(效率高)
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
public class RunnableImpl implements Runnable{
private int ticket=100;
Lock l=new ReentrantLock();
@Override
public void run() {
while (true)
{
l.lock();
if(ticket>0)
{
try{
Thread.sleep(100);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"正在售出第"+ticket+"张票");
ticket--;
}catch(Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
l.unlock();
}
}
}
}
}
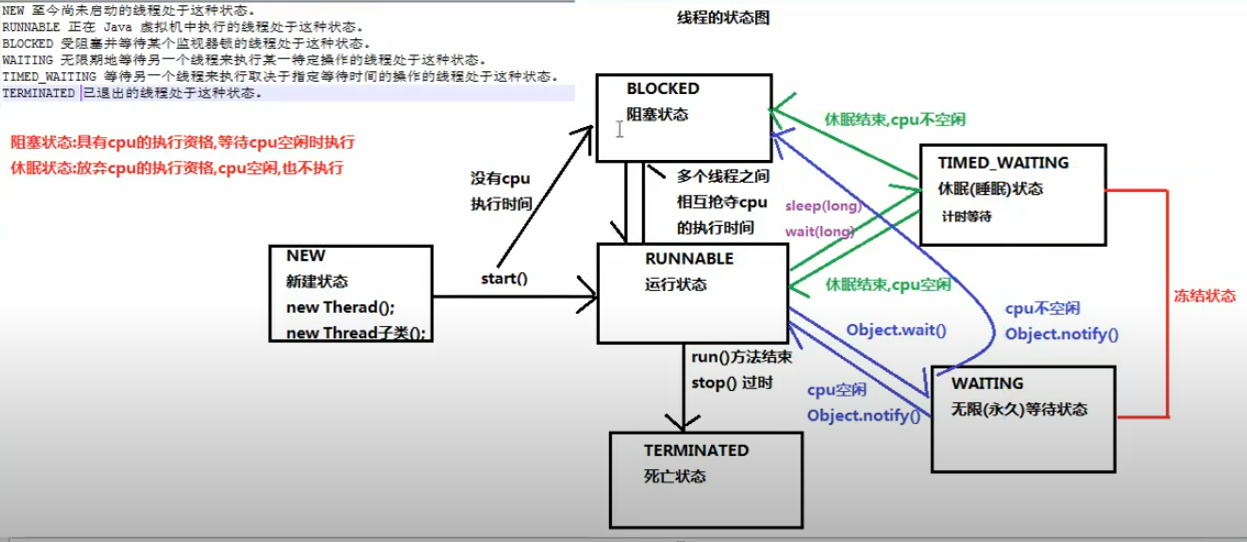
4.线程状态
1.0 概述
2.0等待唤醒案例
分析卖包子案例
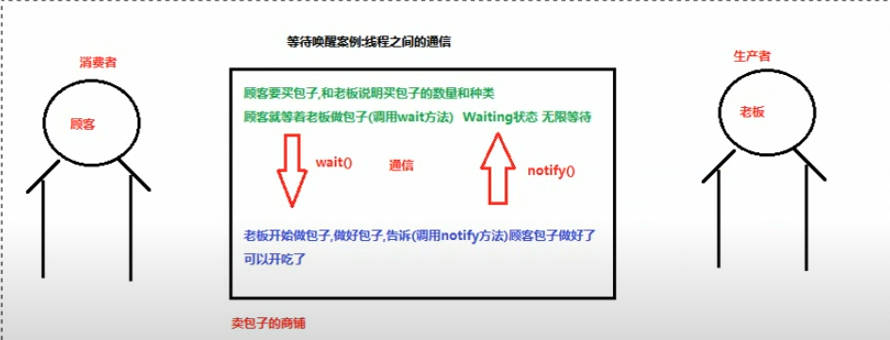
代码实现

public class Sale {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object obj=new Object();//锁对象
//顾客
new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (obj)
{
System.out.println("顾客告诉老板自己的需求");
try {
obj.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("美味的包子已经做好,开吃!");
}
}.start();
//老板
new Thread(){
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (obj)
{
System.out.println("老板5秒做好了包子");
obj.notify();
}
}
}.start();
}
}
打印结果:
顾客告诉老板自己的需求
老板5秒做好了包子
美味的包子已经做好,开吃!
Object类中 wait带参方法以及notify方法


3.等待唤醒机制
案例

public class Baozi {
String Pi;
String Xian;
boolean falg=false;
}
public class Baozipu extends Thread {
private Baozi baozi;
public Baozipu( Baozi baozi) {
this.baozi = baozi;
}
@Override
public void run() {
int count=0;
while(true)
{
synchronized (baozi)
{
//包子状态 有
if(baozi.falg==true)
{
try {
baozi.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//生产包子
if(count%2==0)
{
baozi.Pi="薄皮";
baozi.Xian="猪肉玉米";
}
else
{
baozi.Pi="凉皮";
baozi.Xian="牛肉三鲜";
}
count++;
System.out.println("正在做"+baozi.Pi+baozi.Xian+"的包子");
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);//5秒生产
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
baozi.falg=true;
baozi.notify();
System.out.println(baozi.Pi+baozi.Xian+"的包子已经做好 开吃!");
}
}
}
}

public class Chihuo extends Thread {
private Baozi baozi;
public Chihuo(Baozi baozi) {
this.baozi = baozi;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while(true)
{
synchronized (baozi)
{
if(baozi.falg==false)
{
try {
baozi.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//唤醒后
System.out.println("吃货正在吃:"+baozi.Pi+baozi.Xian+"的包子");
baozi.falg=false;
baozi.notify();
System.out.println("吃货已经吃完,继续生产");
System.out.println("----------------------");
}
}
}
}
测试类(顾客)
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Baozi bz=new Baozi();
new Baozipu(bz).start();
new Chihuo(bz).start();
}
}
5.线程池

public class RunnableImpl implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"正在执行");
}
}
import java.util.concurrent.Executor;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
pool.submit(new RunnableImpl());//pool-1-thread-1正在执行
pool.submit(new RunnableImpl());//pool-1-thread-2正在执行
//只有两个线程 线程池会一直开启 一个线程结束后归还 可以继续使用
pool.submit(new RunnableImpl());//pool-1-thread-1正在执行
pool.shutdown();//销毁线程池
}
}
6.函数式编程思想
1.0 概述

2.0体验Lambda的更优
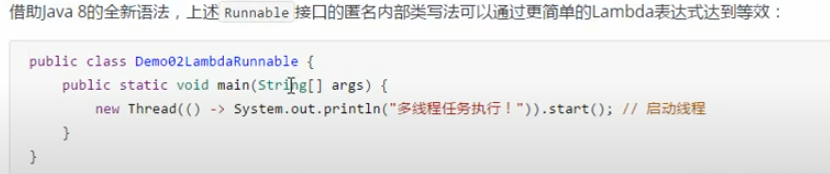
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "正在执行");
}
}.start();
System.out.println("----------");
new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "正在执行");
}).start();
}
}
打印结果:
----------
Thread-1正在执行
Thread-0正在执行
3.0 Lambda标准格式
(1)无参数无返回值

public interface Cook {
public abstract void makefood();
}
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
show(()->{
System.out.println("吃饭啦!德善");
}
);
}
public static void show(Cook cook) {
cook.makefood();
}
}
打印结果:
吃饭啦!德善
(2)有参数有返回值
对年龄进行排序
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Comparator;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person[] person = {new Person("V", 25),
new Person("JK", 23),
new Person("Jin", 27)};
/*
Arrays.sort(person, new Comparator<Person>() {
@Override
public int compare(Person o1, Person o2) {
return o1.getAge()-o2.getAge();//升序
}
});
*/
Arrays.sort(person,(Person o1, Person o2) ->
{
return o1.getAge()-o2.getAge();
});
for (Person person1 : person) {
System.out.println(person1.getName()+" "+person1.getAge());
}
}
}
打印结果:
JK 23
V 25
Jin 27
4.0 lambda可省略

