CGI(通用网关接口),CGI 是Web 服务器运行时外部程序的规范,按CGI 编写的程序可以扩展服务器功能。
CGI 应用程序能与浏览器进行交互,还可通过数据库API 与数据库服务器等外部数据源进行通信,从数据库服务器中获取数据。
格式化为HTML文档后,发送给浏览器,也可以将从浏览器获得的数据放到数据库中。几乎所有服务器都支持CGI,可用任何语言编写CGI。
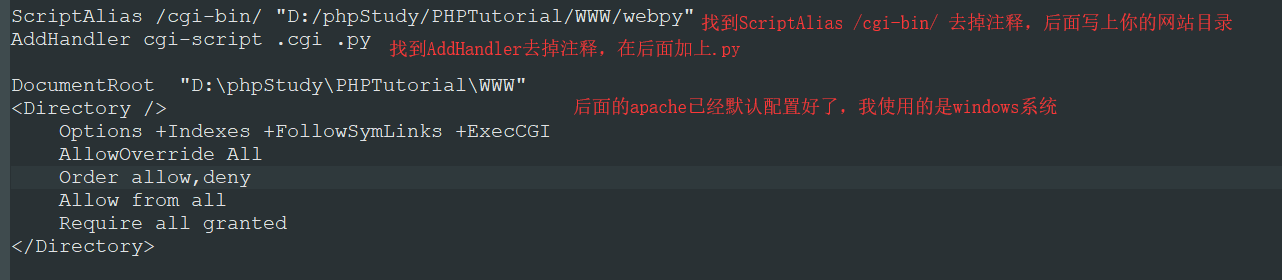
配置让apache支持.py文件,我使用的是phpstudy集成环境,不知道咋回事,windows里面这个斜杠我怎么打都没报错,如果使用的是linux,请遵守交通规则(斜杠别打错了)
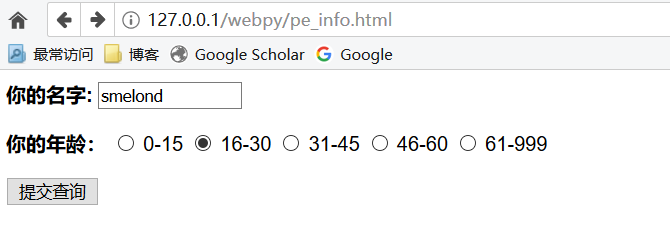
一个简单的 Web 表单从 HTML 代码中可以看到,该表单包括两个输入变量:user 和 age。这两个字段的值将会传到 CGI 脚本pe_info.py 中:
文件名:pe_info.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<title>hello py</title>
<body>
<form method="POST" action="cgi-bin/pe_info.py">
<b>你的名字:</b>
<input type="text" name="user" placeholder="username" size="15">
<p>
<b>你的年龄:</b>
<input type="radio" name="age" value="0-15" checked> 0-15
<input type="radio" name="age" value="16-30"> 16-30
<input type="radio" name="age" value="31-45"> 31-45
<input type="radio" name="age" value="46-60"> 46-60
<input type="radio" name="age" value="61-999"> 61-999
</p>
<input type="submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>
文件名:pe_info.py
#!C:\Users\smelond\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python36-32\python.exe
# _*_ coding:utf-8 _*_
# File_type:返回个人信息
# Filename:pe_info.py
# Author:smelond
import cgi
import cgitb # 若想在浏览器中看到的是 Web 应用程序的回溯信息,而不是“内部服务器错误”,可以使用 cgitb 模块
cgitb.enable()
form = cgi.FieldStorage() # FieldStorage 的实例,包含 user 和 howmany 字段的值
print("Content-Type:text/html\n") # 注意,如果没有这条,可能会提示500错误
print("<title>hello py</title>")
if not 'user' in form:
print("no input name")
else:
user = form["user"].value # 获取变量中的值
age = form["age"].value
print("<h1>%s:%s</h1>" % (user, age))
注意看第一行,我使用的是python3的绝对路径,而不是#!/usr/bin/env python,否则可能会出现500错误
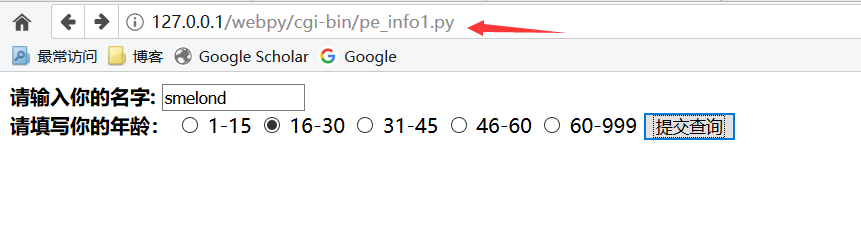
效果:
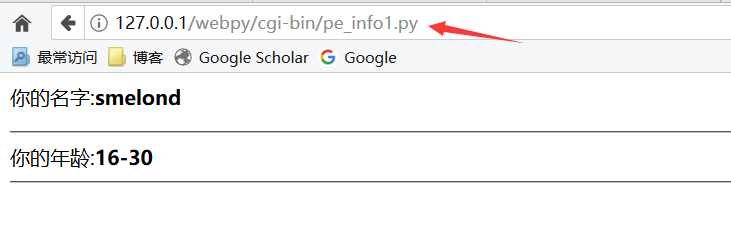
提交之后:
绕过上面的静态文件,将两个文件合并到一个文件内,最终的脚本可以用动态生成的 HTML 文件输出表单和结果页面,并且知道在何时输出哪个页面。
#!C:\Users\anjing\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python36-32\python.exe
# _*_ coding:utf-8 _*_
# File_type:单页面返回提交的个人信息
# Filename:pe_info1.py
# Author:smelond
import cgi
import cgitb
cgitb.enable()
print("Content-Type:text/html\n")
formhtml = """
<html>
<head>
<title>CGI</title>
</head>
<body>
<form method="POST" action="">
<b>请输入你的名字:</b>
<input type="text" name="user" placeholder="username" size="15"><br>
<input type="hidden" name="action" value="edit">
<b>请填写你的年龄:</b>
%s
<input type="submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>
""" # 上面有一个type=hidden用来判断是否提交
fradio = '<input type="radio" name="age" value="%s" %s> %s\n'
def showForm():
friends = []
for i in ("1-15", "16-30", "31-45", "46-60", "60-999"):
checked = ''
if i == "16-30":
checked = "checked"
friends.append(fradio % (str(i), checked, str(i))) # 把这些数字分别写到fradio里面,然后添加到friends列表中
print("%s" % formhtml % "".join(friends)) # 将每个单选按钮用join拆分后放到formhtml里面,然后再放到%s里面,然后打印出来
reshtml = """
<html>
<head><title>rehtml CGI</title></head>
<body>
你的名字:<b>%s</b><p><hr>
你的年龄:<b>%s</b><hr>
</body>
</html>
"""
def doResults(user, howmany):
print(reshtml % (user, howmany))
def process():
form = cgi.FieldStorage()
if "user" in form:
user = form["user"].value
else:
user = "no user"
if "age" in form:
age = form["age"].value
else:
age = 0
if "action" in form: # 当我们点击了提交,FieldStorage实例里面会有MiniFieldStorage('action', 'edit'),上面说过hidden用来判断是否提交
doResults(user, age)
else: # 如果过没有action,表示我们还没有提交,FieldStorage里面什么都没有,所以执行showForm()函数
showForm()
if __name__ == '__main__':
process()