Numpy
Numpy 是 Python 数据科学计算的核心库,提供了高性能的多维数组对象及处理数组的工具
使用方式
import numpy as np
数组
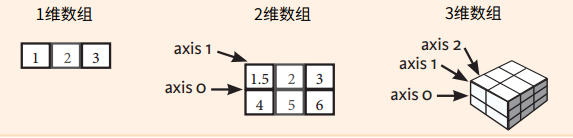
生成数组
简单生成
a = np.array([1, 2, 3]) # <class 'numpy.ndarray'> # [1 2 3] a = np.array([1, '2', 3]) # 取值为字符串 # <class 'numpy.ndarray'> # ['1' '2' '3'] a = np.array([1, 2.0, 3]) # 取值去float # <class 'numpy.ndarray'> # [1. 2. 3.]
dtype类型
a = np.array([1, 2.0, 3],dtype=np.str) # <class 'numpy.ndarray'> # ['1' '2.0' '3'] # 其他类型 # np.int64 带符号的64位整数 # np.float32 标准双精度浮点数 # np.complex 显示为128位浮点数的复数 # np.bool 布尔值:True值和False值 # np.object Python对象 # np.string_ 固定长度字符串 # np.unicode_ 固定长度Unicode
copy参数
# copy参数 默认True a = np.array([1, '2', 3]) b = np.array(a, copy=True) c = np.array(a, copy=False) # 635743528800 # 635743684528 # 635743528800
初始化占位符
# 3行4列 a = np.zeros((3, 4)) # <class 'numpy.ndarray'> # [[0. 0. 0. 0.] # [0. 0. 0. 0.] # [0. 0. 0. 0.]] # 2行3列4纵 a = np.ones((2, 3, 4,2), dtype=np.int16) # <class 'numpy.ndarray'> # [[[1 1 1 1] # [1 1 1 1] # [1 1 1 1]] # # [[1 1 1 1] # [1 1 1 1] # [1 1 1 1]]] # 创建均匀间隔的数组(步进值) a = np.arange(10, 25, 5) # <class 'numpy.ndarray'> # [10 15 20] # 创建均匀间隔的数组(样本数) a = np.linspace(0, 2, 9) # <class 'numpy.ndarray'> # [0. 0.25 0.5 0.75 1. 1.25 1.5 1.75 2. ] # 创建常数数组 a = np.full((2,2),7) # <class 'numpy.ndarray'> # [[7 7] # [7 7]] # 创建2x2单位矩阵 a = np.eye(2) # <class 'numpy.ndarray'> # [[1. 0.] # [0. 1.]] # 创建随机值的数组 a = np.random.random((2,2)) # <class 'numpy.ndarray'> # [[0.43922179 0.48453874] # [0.753194 0.09264839]] # 创建空数组 a = np.empty((3,2)) # <class 'numpy.ndarray'> # [[1.39069238e-309 1.39069238e-309] # [1.39069238e-309 1.39069238e-309] # [1.39069238e-309 1.39069238e-309]]
输入输出
保存/读取
# 保存为npy文件
a = np.full((10,10),7)
# 保存
np.save('my_array', a)
# 读取
np.load('my_array.npy')
# 保存文本文档
np.savetxt("myarray.txt", a, delimiter=",")
# 读取
np.loadtxt("myarray.txt")
# 读取excel
np.genfromtxt("my_fle.csv", delimiter=',')
数组信息
a = np.zeros((3, 4)) # [[0. 0. 0. 0.] # [0. 0. 0. 0.] # [0. 0. 0. 0.]] # 数组形状,几行几列 print(a.shape) # (3, 4) # 数组长度 print(len(a)) # 3 # 几维数组 print(a.ndim) # 2 # 数组有多少元素 print(a.size) # 12 # 数据类型 print(a.dtype) # float64 # 数据类型的名字 print(a.dtype.name) # float64 # 数据类型转换 print(a.astype(int)) # [[0 0 0 0] # [0 0 0 0] # [0 0 0 0]]
索引、切片、比较
切片
import numpy as np
matrix = np.array([
[5, 10, 15],
[20, 25, 30],
[35, 40, 45]
])
# 取所有行的第2列
print(matrix[:,1])
# [10 25 40]
# 取所有行的前1、2列
print(matrix[:,0:2])
# [[ 5 10]
# [20 25]
# [35 40]]
# 取2、3行的前1、2列
print(matrix[1:3,0:2])
# [[20 25]
# [35 40]]
比较
import numpy as np
# 获取比较结果
matrix = np.array([
[5, 10, 15],
[20, 25, 30],
[35, 40, 45]
])
print(matrix == 25)
# [[False False False]
# [False True False]
# [False False False]]
# 根据比较结果取值
vector = np.array([5, 10, 15, 20])
equal_to_ten = (vector == 10)
print(equal_to_ten)
print(vector[equal_to_ten])
# [False True False False]
# [10]
# 根据比较结果切片取值
matrix = np.array([
[5, 10, 15],
[20, 25, 30],
[35, 40, 45]
])
second_column_25 = (matrix[:,1] == 25)
print(second_column_25)
print(matrix[second_column_25, :])
# [False True False]
# [[20 25 30]]
# 与操作 去比较结果
vector = np.array([5, 10, 15, 20])
equal_to_ten_and_five = (vector == 10) & (vector == 5)
print(equal_to_ten_and_five)
# [False False False False]
# 或操作 去比较结果
vector = np.array([5, 10, 15, 20])
equal_to_ten_or_five = (vector == 10) | (vector == 5)
print(equal_to_ten_or_five)
# [ True True False False]
# 根据比较结果赋值
vector = np.array([5, 10, 15, 20])
equal_to_ten_or_five = (vector == 10) | (vector == 5)
vector[equal_to_ten_or_five] = 50
print(vector)
# [50 50 15 20]
数组计算
聚合函数
# 数据汇总
vector = np.array([5, 10, 15, 20])
print(vector.sum())
# 50
# 二维矩阵汇总
matrix = np.array([
[5, 10, 15],
[20, 25, 30],
[35, 40, 45]
])
print(matrix.sum())
# 225
# 二维横向汇总
print(matrix.sum(axis=1))
# [ 30 75 120]
# 二维竖向汇总
print(matrix.sum(axis=0))
# [60 75 90]
数组运算
a = np.array([20, 30, 40, 50])
b = np.arange(4)
print(a)
print(b)
# [20 30 40 50]
# [0 1 2 3]
# 减
c = a - b
print(c)
# [20 29 38 47]
# 加
c = a + b
print(c)
# [20 31 42 53]
# 乘
c = a * b
print(c)
# [ 0 30 80 150]
# 除
c = b / a
print(c)
# [0. 0.03333333 0.05 0.06 ]
# 2次幂
print(b**2)
# [0 1 4 9]
# 点积 https://www.jianshu.com/p/482abac8798c
A = np.array( [[1,1],
[0,1]] )
B = np.array( [[2,0],
[3,4]] )
print(A)
print(B)
print(A.dot(B))
print(np.dot(A, B))
# [[1 1]
# [0 1]]
# [[2 0]
# [3 4]]
# [[5 4]
# [3 4]]
# [[5 4]
# [3 4]]
import numpy as np
B = np.arange(3)
print(B)
# [0 1 2]
# 幂
print(np.exp(B))
# [1. 2.71828183 7.3890561 ]
# 平方根
print(np.sqrt(B))
# [0. 1. 1.41421356]
数组操作
import numpy as np # floor向下取整 a = np.floor(10*np.random.random((3,4))) print(a) # [[1. 5. 3. 3.] # [3. 3. 2. 6.] # [4. 9. 5. 3.]] # ravel合为一行 print(a.ravel()) # [1. 5. 3. 3. 3. 3. 2. 6. 4. 9. 5. 3.] # 更换shape形状 a.shape = (6, 2) print(a) # [[1. 5.] # [3. 3.] # [3. 3.] # [2. 6.] # [4. 9.] # [5. 3.]] # 横竖转换 print(a.T) # [[1. 3. 3. 2. 4. 5.] # [5. 3. 3. 6. 9. 3.]] # -1 默认值 print(a.reshape(3,-1)) # [[1. 5. 3. 3.] # [3. 3. 2. 6.] # [4. 9. 5. 3.]] # 拼接 a = np.floor(10*np.random.random((2,2))) b = np.floor(10*np.random.random((2,2))) print(a) # [[5. 7.] # [2. 9.]] print(b) # [[7. 4.] # [7. 7.]] print(np.hstack((a,b))) # 横向拼接 # [[5. 7. 7. 4.] # [2. 9. 7. 7.]] print(np.vstack((a,b))) # 纵向拼接 # [[5. 7.] # [2. 9.] # [7. 4.] # [7. 7.]] # 分割 a = np.floor(10*np.random.random((2,12))) print(a) # [[4. 7. 8. 2. 0. 1. 5. 7. 1. 2. 1. 2.] # [5. 8. 9. 2. 5. 5. 8. 9. 5. 4. 7. 8.]] print(np.hsplit(a,3)) # 横向切割3份 # [array([[4., 7., 8., 2.], # [5., 8., 9., 2.]]), array([[0., 1., 5., 7.], # [5., 5., 8., 9.]]), array([[1., 2., 1., 2.], # [5., 4., 7., 8.]])] print(np.vsplit(a,2)) # 横向切割3份 # [array([[4., 7., 8., 2., 0., 1., 5., 7., 1., 2., 1., 2.]]), array([[5., 8., 9., 2., 5., 5., 8., 9., 5., 4., 7., 8.]])] print(np.hsplit(a,(3,4))) # 横向切割3,4 # [array([[9., 3., 0.], # [1., 0., 4.]]), array([[7.], # [5.]]), array([[8., 5., 7., 7., 4., 9., 8., 2.], # [6., 7., 6., 4., 9., 5., 9., 3.]])]
拷贝
# 赋值 a = np.arange(12) b = a # a and b are two names for the same ndarray object # b is a # True b.shape = 3,4 print(a.shape) print(id(a)) print(id(b)) # (3, 4) # 115753432 # 115753432 # 浅拷贝 c = a.view() # c is a # Flase c.shape = 2,6 #print a.shape c[0,4] = 1234 print(a) # [[ 0 1 2 3] # [1234 5 6 7] # [ 8 9 10 11]] # 深拷贝 d = a.copy() # d is a # Flase d[0,0] = 9999 print(d) print(a) # [[9999 1 2 3] # [1234 5 6 7] # [ 8 9 10 11]] # [[ 0 1 2 3] # [1234 5 6 7] # [ 8 9 10 11]]