1、文件首行用来指定编码方式:
#-*- encoding:utf-8 -*-
2、变量:
(1)必须是由数字、字母、下划线任意组合,且不能数字开头。
(2)不能是python中的关键字['and', 'as', 'assert', 'break', 'class', 'continue', 'def', 'del', 'elif','else', 'except', 'exec', 'finally', 'for', 'from',
'global', 'if', 'import', 'in', 'is', 'lambda', 'not', 'or', 'pass', 'print', 'raise', 'return', 'try', 'while', 'with', 'yield']
(3)变量名必须具有可描述性。建议用下划线隔开,例如:age_of_oldboy。
(4)不能是中文。
#设置变量x,y x = (1+2+3+4) print(x) print(x*5) y = x*5 print (y+100-45+2)
#变量指向 age1 = 12 age2 = age1 age3 = age2 age2 = 100 print (age1,age2,age3)
3、常量:
(1)π
(2)大写一般为常量
(3)其他
BIR_OF_CHINA = 19491001
4、注释:
单行注释:#
多行注释:'''注释内容''' ,"""注释内容"""
5、基础数据类型初识:
print (x,type(x)) #判断数字类型
(1)int 运算符:+, - ,*, / ,%, ** ,//。
(2)str python当中凡是用引号引起来的都是字符串。
print("i'm a student") #字符串可以用单引号/双引号包括,如果字符串内有单引号,就用双引号包括,反之则用单引号。 a = 'steven' b = 'lily' c = a + b #字符串可相加:字符串的拼接。 print(c) $stevenlily d = a * 2 #字串符可想乘:字符串打印几次 str * int print (d)
msg = ''' 锄禾日当午, 汗滴禾下土。 谁知盘中餐, 粒粒皆辛苦。 ''' #三个单引号引起来并予以赋值变量,变成了一个长字符串,而不是注释的作用了。 print(msg)
(3)bool 返回 Ture or False
a = 3 b = 2 print (a>b) #判断True False
6、用户交互:input
(1)等待输入
(2)将你输入的内容赋值给了前面的变量
(3)input出来的数据类型全部是str
#用户交互 name = input ('请输入你的名字:') age = input ('请输入你的年龄:') print ('我的名字是'+name,'我的年龄是'+age+'岁') $请输入你的名字:x 请输入你的年龄:y 我的名字是x 我的年龄是y岁
7、条件语句
(1)if:
if...if #两个条件都会执行
if...elif #若if条件成立则不会执行elif条件。
if 5 > 4 : print (666) print (777) print (111) if True : print (666) print (777) if False : print (555) print(777)
if 4 > 5 : print ('我请你喝酒') else : print ('喝什么酒') if 4 > 5 : print ('我请你喝酒') print ('喝什么酒')
num = input ('请输入您猜的数字:') if num == '1' : print ('恭喜你,答对了') elif num == '2' : print ('恭喜你,答对了') elif num == '3' : print ('恭喜你,答对了') else : print ('你猜错了')
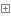
scroe = int(input('请输入您的分数:')) #int(str)改变数据类型 if scroe >= 90 : print ('A') elif scroe >= 80 : print ('B') elif scroe >= 70 : print ('C') elif scroe >= 60 : print ('D') else : print ("you're fail!")
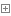
username = input ('请输入用户名:') password = input ('请输入密码:') if username == 'xinxin' : if password == 'abcd1234' : print ('欢迎您!!!') else : print ('密码错误!!!') else : print ('无此账号!!!')
(2)while
a、无限循环
#无限循环 print('开始') while True : print('我们不一样') print('在人间') print('痒') ptint('结束')
b、终止循环:
改变条件,使其不成立。
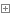
#方法一: count = 1 flag = True #标志位 while flag : print (count) count = count + 1 if count > 100 : flag = False #方法二: count = 1 while count <= 100 : print (count) count = count + 1 #方法三 count = 1 while 1 : print (count) count = count + 1 if count > 100 : break
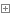
# i = 0 # sum = 0 # while i < 100: # i = i + 1 # sum = sum + i # print(sum)
print('开始') while True: print('222') print('333') break print('444') print('结束')
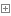
i = 0 while 1: i = i + 1 if i > 100: break print(i)
continue。跳出循环重新开始执行
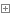
print ('开始') count = 1 while count <= 100 : print (count) count = count + 1 continue
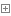
i = 0 while i < 100: i = i +1 if 95 > i > 5: continue print(i)
(3)while循环使用else语句
count = 0 while count < 5: print(count,"小于5") count +=1 else: print(count,"大于或等于5")
(4)for 循环:
ss = '1A2B3C4D5E6F!?' for i in ss: # i是变量,ss可以是列表,元组,字典。i 在 ss中有限循环。 print(i) #场景应用:敏感词。 sss = '你好,hello!' if 'hello' in sss: print('您的评论中有英文')
课后练习
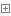
#方法1: count = 0 while count < 101: print(count) count = count + 2 #方法2: count = 1 while count < 101: if count % 2 == 0: print (count) count = count + 1 #方法3: count = 1 while True : if count % 2 == 0 : print (count) count = count + 1 if count >=101 : break
#方法1: count = 1 while count < 101: print(count) count = count + 2 #count += 2 #方法2: count = 1 while count < 101: if count % 2 == 1: print (count) count = count + 1 #方法3: count = 1 while True: if count % 2 == 1: print (count) count = count + 1 if count >=101: break
#方法1: i = 1 sum1 = 0 sum2 = 0 while i < 100: if i % 2 == 0: sum1 = sum1 + i else: sum2 = sum2 + i i = i + 1 print(sum2 - sum1) #方法2: i = 1 sum = 0 while i < 100: if i % 2 == 0: sum = sum - i else: sum = sum + i i = i + 1 print(sum) #方法3: i = 0 j = -1 sum = 0 while i < 99: i = i + 1 j = -j if i % 2 == 0: sum = sum - i else: sum = sum + i print(sum)
# 方法1: i = 1 sum1 = 0 while i < 100: if i == 88: i = i + 1 continue elif i % 2 != 0: sum1 = sum1 + i else: sum1 = sum1 - i i = i + 1 print(sum1) #方法2: i = 0 j = -1 sum = 0 while i < 99: i = i + 1 j = -j if i == 88: continue else: sum = sum + i * j print(sum)
# 计算1 -2 + 3 ... - 99 中除了88以外的所有数的总和 i = 1 sum1 = 0 while i < 100: if i == 88: i = i + 1 continue elif i % 2 != 0: if i == 99: i = i + 1 sum1 = sum1 - i sum1 = sum1 + i else: sum1 = sum1 - i i = i + 1 print(sum1)
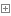
#方法1: count = 0 while count < 10: count = count + 1 if count == 7: print ('') else: print(count) #方法2:最优解 count = 0 while count < 10: count = count + 1 if count == 7: continue print(count) #方法3: count = 0 while count < 10: count = count + 1 if count == 7: pass else: print(count)
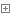
i = 0 while i < 3: username = input ('请输入用户名:') password = input ('请输入密码:') if username == 'xinxin' and password == 'abcd1234' : print ('欢迎您!!!') else : print ('错误!请重新输入') i += 1
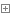
name = 'xinxin' pwd = '123456' i1 = 3 i2 = 3 while i2 > 0: mz = input('请输入用户名:') i1 = 3 if mz == name: while i1 > 0: mm = input('请输入密码:') i1 = i1 - 1 if mm == pwd: print('欢迎您,登录成功') break else: print('请重新输入密码') if i1 == 0: print('次数已经用完,请重新登录。') break else: print('用户名错误,请重新输入:') i2 = i2 - 1 if i2 == 0: print('次数已经用完,请重新登录。') break
8、格式化输出:
(1)%占位符
%s 字符串
%d 数字
%% 百分号输出
name = input('请输入姓名:') age = input('请输入年龄:') job = input('请输入工作:') hobbie = input('请输入兴趣:') msg = '''--------------- info of %s --------------- name: %s age: %d job: %s hobbie:%s 我的心情指数:100%% --------------- end ---------------''' %(name,name,int(age),job,hobbie) print(msg)
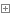
username = 'xinxin' password = 'abcd1234' i = 0 while i < 3: name = input('请输入账号:') psw = input('请输入密码:') if name == username and psw == password: print('欢迎您') break else: print('账号密码错误,请重新输入,剩下%d次机会' % (2 - i)) if (2-i) == 0: result =input('是否还想再试试?Yes') if result == 'Yes': i = 0 continue i = i + 1 else:print('goodbye') #思考自己写的这个如何进入上述代码的循环 username = 'xinxin' password = 'abcd1234' i = 0 while i < 3: name = input('请输入账号:') psw = input('请输入密码:') if name == username and psw == password: print('欢迎您') break else: if name == username and psw != password: print('密码错误,剩下%d次机会' % (2 - i)) elif name != username and psw != password: print('账号密码错误,请重新输入,剩下%d次机会' % (2 - i)) i += 1
(2)format
# format 格式化输出的三种玩法: # 第一种: s3 = '''my name is {}, i am {} year old, i like {}, again, i am {}.'''.format('xxx','02','playgame','xxx') print(s3) # 第二种: s4 = '''my name is {0}, i am {1} year old, i like {2}, again, i am {0}.'''.format('xxx','02','playgame') print(s4) n = input('name:') a = input('age:') h = input('hobby:') s4 = '''my name is {0}, i am {1} year old, i like {2}, again, i am {0}.'''.format(n,a,h) print(s4) # 第三种: n = input('name:') a = input('age:') h = input('hobby:') s5 = '''my name is {name}, i am {age} year old, i like {hobby}, again, i am {name}.'''.format(name=n,age=a,hobby=h) print(s5)
9、初始编码:电脑的传输,储存实际上都是用0和1来表示。
(1)ASCII码:设计之初只为美国本土考虑,7位足以,作者预留了1位(bit),遂形成了8位表示一个字节(byte),且所有的ASCII码最左边一位全部都是“0”
8bit == 1byte
1024byte == 1kb
1024kb == 1MB
1024MB == 1GB
1024GB == 1TB
|
Bin(二进制)
|
Oct(八进制) |
Dec(十进制)
|
Hex(十六进制)
|
缩写/字符
|
解释
|
|
0000 0000
|
0
|
0
|
00
|
NUL(null)
|
空字符
|
|
0000 0001
|
1
|
1
|
01
|
SOH(start of headline)
|
标题开始
|
|
0000 0010
|
2
|
2
|
02
|
STX (start of text)
|
正文开始
|
|
0000 0011
|
3
|
3
|
03
|
ETX (end of text)
|
正文结束
|
|
0000 0100
|
4
|
4
|
04
|
EOT (end of transmission)
|
传输结束
|
|
0000 0101
|
5
|
5
|
05
|
ENQ (enquiry)
|
请求
|
|
0000 0110
|
6
|
6
|
06
|
ACK (acknowledge)
|
收到通知
|
|
0000 0111
|
7
|
7
|
07
|
BEL (bell)
|
响铃
|
|
0000 1000
|
10
|
8
|
08
|
BS (backspace)
|
退格
|
|
0000 1001
|
11
|
9
|
09
|
HT (horizontal tab)
|
水平制表符
|
|
0000 1010
|
12
|
10
|
0A
|
LF (NL line feed, new line)
|
换行键
|
|
0000 1011
|
13
|
11
|
0B
|
VT (vertical tab)
|
垂直制表符
|
|
0000 1100
|
14
|
12
|
0C
|
FF (NP form feed, new page)
|
换页键
|
|
0000 1101
|
15
|
13
|
0D
|
CR (carriage return)
|
回车键
|
|
0000 1110
|
16
|
14
|
0E
|
SO (shift out)
|
不用切换
|
|
0000 1111
|
17
|
15
|
0F
|
SI (shift in)
|
启用切换
|
|
0001 0000
|
20
|
16
|
10
|
DLE (data link escape)
|
数据链路转义
|
|
0001 0001
|
21
|
17
|
11
|
DC1 (device control 1)
|
设备控制1
|
|
0001 0010
|
22
|
18
|
12
|
DC2 (device control 2)
|
设备控制2
|
|
0001 0011
|
23
|
19
|
13
|
DC3 (device control 3)
|
设备控制3
|
|
0001 0100
|
24
|
20
|
14
|
DC4 (device control 4)
|
设备控制4
|
|
0001 0101
|
25
|
21
|
15
|
NAK (negative acknowledge)
|
拒绝接收
|
|
0001 0110
|
26
|
22
|
16
|
SYN (synchronous idle)
|
同步空闲
|
|
0001 0111
|
27
|
23
|
17
|
ETB (end of trans. block)
|
结束传输块
|
|
0001 1000
|
30
|
24
|
18
|
CAN (cancel)
|
取消
|
|
0001 1001
|
31
|
25
|
19
|
EM (end of medium)
|
媒介结束
|
|
0001 1010
|
32
|
26
|
1A
|
SUB (substitute)
|
代替
|
|
0001 1011
|
33
|
27
|
1B
|
ESC (escape)
|
换码(溢出)
|
|
0001 1100
|
34
|
28
|
1C
|
FS (file separator)
|
文件分隔符
|
|
0001 1101
|
35
|
29
|
1D
|
GS (group separator)
|
分组符
|
|
0001 1110
|
36
|
30
|
1E
|
RS (record separator)
|
记录分隔符
|
|
0001 1111
|
37
|
31
|
1F
|
US (unit separator)
|
单元分隔符
|
|
0010 0000
|
40
|
32
|
20
|
(space)
|
空格
|
|
0010 0001
|
41
|
33
|
21
|
!
|
叹号 |
|
0010 0010
|
42
|
34
|
22
|
"
|
双引号 |
|
0010 0011
|
43
|
35
|
23
|
#
|
井号 |
|
0010 0100
|
44
|
36
|
24
|
$
|
美元符 |
|
0010 0101
|
45
|
37
|
25
|
%
|
百分号 |
|
0010 0110
|
46
|
38
|
26
|
&
|
和号 |
|
0010 0111
|
47
|
39
|
27
|
'
|
闭单引号 |
|
0010 1000
|
50
|
40
|
28
|
(
|
开括号
|
|
0010 1001
|
51
|
41
|
29
|
)
|
闭括号
|
|
0010 1010
|
52
|
42
|
2A
|
*
|
星号 |
|
0010 1011
|
53
|
43
|
2B
|
+
|
加号 |
|
0010 1100
|
54
|
44
|
2C
|
,
|
逗号 |
|
0010 1101
|
55
|
45
|
2D
|
-
|
减号/破折号 |
|
0010 1110
|
56
|
46
|
2E
|
.
|
句号 |
|
00101111
|
57
|
47
|
2F
|
/
|
斜杠 |
|
00110000
|
60
|
48
|
30
|
0
|
数字0 |
|
00110001
|
61
|
49
|
31
|
1
|
数字1 |
|
00110010
|
62
|
50
|
32
|
2
|
数字2 |
|
00110011
|
63
|
51
|
33
|
3
|
数字3 |
|
00110100
|
64
|
52
|
34
|
4
|
数字4 |
|
00110101
|
65
|
53
|
35
|
5
|
数字5 |
|
00110110
|
66
|
54
|
36
|
6
|
数字6 |
|
00110111
|
67
|
55
|
37
|
7
|
数字7 |
|
00111000
|
70
|
56
|
38
|
8
|
数字8 |
|
00111001
|
71
|
57
|
39
|
9
|
数字9 |
|
00111010
|
72
|
58
|
3A
|
:
|
冒号 |
|
00111011
|
73
|
59
|
3B
|
;
|
分号 |
|
00111100
|
74
|
60
|
3C
|
<
|
小于 |
|
00111101
|
75
|
61
|
3D
|
=
|
等号 |
|
00111110
|
76
|
62
|
3E
|
>
|
大于 |
|
00111111
|
77
|
63
|
3F
|
?
|
问号 |
|
01000000
|
100
|
64
|
40
|
@
|
电子邮件符号 |
|
01000001
|
101
|
65
|
41
|
A
|
大写字母A |
|
01000010
|
102
|
66
|
42
|
B
|
大写字母B |
|
01000011
|
103
|
67
|
43
|
C
|
大写字母C |
|
01000100
|
104
|
68
|
44
|
D
|
大写字母D |
|
01000101
|
105
|
69
|
45
|
E
|
大写字母E |
|
01000110
|
106
|
70
|
46
|
F
|
大写字母F |
|
01000111
|
107
|
71
|
47
|
G
|
大写字母G |
|
01001000
|
110
|
72
|
48
|
H
|
大写字母H |
|
01001001
|
111
|
73
|
49
|
I
|
大写字母I |
|
01001010
|
112
|
74
|
4A
|
J
|
大写字母J |
|
01001011
|
113
|
75
|
4B
|
K
|
大写字母K |
|
01001100
|
114
|
76
|
4C
|
L
|
大写字母L |
|
01001101
|
115
|
77
|
4D
|
M
|
大写字母M |
|
01001110
|
116
|
78
|
4E
|
N
|
大写字母N |
|
01001111
|
117
|
79
|
4F
|
O
|
大写字母O |
|
01010000
|
120
|
80
|
50
|
P
|
大写字母P |
|
01010001
|
121
|
81
|
51
|
Q
|
大写字母Q |
|
01010010
|
122
|
82
|
52
|
R
|
大写字母R |
|
01010011
|
123
|
83
|
53
|
S
|
大写字母S |
|
01010100
|
124
|
84
|
54
|
T
|
大写字母T |
|
01010101
|
125
|
85
|
55
|
U
|
大写字母U |
|
01010110
|
126
|
86
|
56
|
V
|
大写字母V |
|
01010111
|
127
|
87
|
57
|
W
|
大写字母W |
|
01011000
|
130
|
88
|
58
|
X
|
大写字母X |
|
01011001
|
131
|
89
|
59
|
Y
|
大写字母Y |
|
01011010
|
132
|
90
|
5A
|
Z
|
大写字母Z |
|
01011011
|
133
|
91
|
5B
|
[
|
开方括号 |
|
01011100
|
134
|
92
|
5C
|
\
|
反斜杠 |
|
01011101
|
135
|
93
|
5D
|
]
|
闭方括号 |
|
01011110
|
136
|
94
|
5E
|
^
|
脱字符 |
|
01011111
|
137
|
95
|
5F
|
_
|
下划线 |
|
01100000
|
140
|
96
|
60
|
`
|
开单引号 |
|
01100001
|
141
|
97
|
61
|
a
|
小写字母a |
|
01100010
|
142
|
98
|
62
|
b
|
小写字母b |
|
01100011
|
143
|
99
|
63
|
c
|
小写字母c |
|
01100100
|
144
|
100
|
64
|
d
|
小写字母d |
|
01100101
|
145
|
101
|
65
|
e
|
小写字母e |
|
01100110
|
146
|
102
|
66
|
f
|
小写字母f |
|
01100111
|
147
|
103
|
67
|
g
|
小写字母g |
|
01101000
|
150
|
104
|
68
|
h
|
小写字母h |
|
01101001
|
151
|
105
|
69
|
i
|
小写字母i |
|
01101010
|
152
|
106
|
6A
|
j
|
小写字母j |
|
01101011
|
153
|
107
|
6B
|
k
|
小写字母k |
|
01101100
|
154
|
108
|
6C
|
l
|
小写字母l |
|
01101101
|
155
|
109
|
6D
|
m
|
小写字母m |
|
01101110
|
156
|
110
|
6E
|
n
|
小写字母n |
|
01101111
|
157
|
111
|
6F
|
o
|
小写字母o |
|
01110000
|
160
|
112
|
70
|
p
|
小写字母p |
|
01110001
|
161
|
113
|
71
|
q
|
小写字母q |
|
01110010
|
162
|
114
|
72
|
r
|
小写字母r |
|
01110011
|
163
|
115
|
73
|
s
|
小写字母s |
|
01110100
|
164
|
116
|
74
|
t
|
小写字母t |
|
01110101
|
165
|
117
|
75
|
u
|
小写字母u |
|
01110110
|
166
|
118
|
76
|
v
|
小写字母v |
|
01110111
|
167
|
119
|
77
|
w
|
小写字母w |
|
01111000
|
170
|
120
|
78
|
x
|
小写字母x |
|
01111001
|
171
|
121
|
79
|
y
|
小写字母y |
|
01111010
|
172
|
122
|
7A
|
z
|
小写字母z |
|
01111011
|
173
|
123
|
7B
|
{
|
开花括号 |
|
01111100
|
174
|
124
|
7C
|
|
|
垂线 |
|
01111101
|
175
|
125
|
7D
|
}
|
闭花括号 |
|
01111110
|
176
|
126
|
7E
|
~
|
波浪号 |
|
01111111
|
177
|
127
|
7F
|
DEL (delete)
|
(2) 万国码(Unicode)
ASCII码为了解决全球化文字问题,创建了一个万国码Unicode。用4个字节表示一个汉字。
后升级成为UTF-8。
gbk:中国国产,只能用于中文和ASCII码的文字。
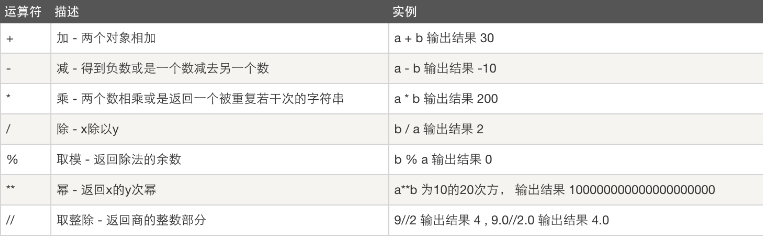
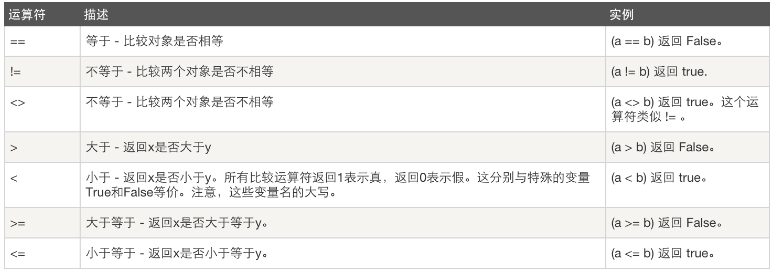
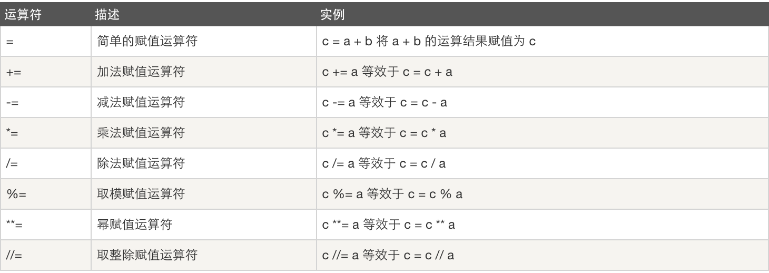
10、 运算符:以下假设变量:a=10,b=20
(1)算数运算
(2)比较运算:
(3)赋值运算:
(4)逻辑运算:

在没有()的情况下not 优先级高于 and,and优先级高于or,即优先级关系为( )>not>and>or,同一优先级从左往右计算。
# int转换成bool时,该值为非0时,为True,否则为False。 print(bool(23)) $True print(bool(0)) $ False # bool转换成int时,只有1和0 print(bool(true)) $1 print(bool(False)) $0
# x or y , x 为 True , 则返回 x (x为非0) print(1 or 2) $ 1 print(3 or 2) $ 3 print(0 or 2) $ 2 print(0 or 100) $ 100 # x and y , x 为 True , 则返回 x (and则与or的规则相反) print(1 and 2) $ 2 print(3 and 2) $ 2 print(0 and 2) $ 0 print(0 and 100) $ 0 # 面试题举例 print(2 or 100 or 3 or 4) $ 2 print(0 or 4 and 3 or 2) $ 3 print(1 > 2 and 3 or 4 and 3 > 2) $True '''运算过程如下: False(0) and 3 or 4 and True(1) False or Ture True '''
(5)Python运算符优先级
以下表格列出了从最高到最低优先级的所有运算符:
| 运算符 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| ** | 指数 (最高优先级) |
| ~ + - | 按位翻转, 一元加号和减号 (最后两个的方法名为 +@ 和 -@) |
| * / % // | 乘,除,取模和取整除 |
| + - | 加法减法 |
| >> << | 右移,左移运算符 |
| & | 位 'AND' |
| ^ | | 位运算符 |
| <= < > >= | 比较运算符 |
| <> == != | 等于运算符 |
| = %= /= //= -= += *= **= | 赋值运算符 |
| is is not | 身份运算符 |
| in not in | 成员运算符 |
| not and or | 逻辑运算符 |
10、数据类型:
(1)int:用于计算。
(2)bool:True or False,用于判断。
# 工作中常用的 while True: pass while 1: #1的效率要更高。 pass # str 转 bool。为空字符串都是True,空就是什么都不输入,不是空格。 if s: #即表示 if s == " print('你输入的为空,请重新输入') else: pass
(3)str:存储少量数据,进行操作。用引号 ' str ' 包括。
索引与切片:
# 索引,根据字符串序号来进行索引,从左至右,从 0 开始,1 2 3 4 5 ... # 从右至左,从 -1 开始,-1 -2 -3 -4 -5 。 s = 'ABCDEFGH' s1 = s[0] # 语法:变量名[序号] print(s1) # $ A s2 = s[-2] print(s2) # $ G #切片,顾头不顾尾。 s = 'ABCDEFGH' s3 = s[0:4] # 序号4是取不到的。 print(s2) # $ ABC s4 = s[-3:-1] print(s4) # $ FG #加步长 变量名[首:尾:步长] s = 'ABCDEFGH' s5 = s[0:5:2] print(s5) # $ ACE s = 'ABCDEFGH' s6 = s[-1:-6:-2] print(s6) # $ HFD s7 = s[5:2:-1] print(s7) # $ FED s8 = s[-1:-4:-1] print(s8) # $ HGF s9 = s[0:] print(s8) # $ HGF #取全部值。 s = 'ABCDEFGH' s9 = s[0:] print(s9) # $ ABCDEFGH s10 = s[::-1] print(s10) # $ HGFEDCBA
字符串其他操作
s = 'xCm xl xXx' print(s.capitalize()) # 首字母大写 print(s.upper()) # 全大写 print(s.lower()) # 全小写 print(s.swapcase()) # 大小写翻转 print(s.title()) # 每个隔开(特殊字符或数字)的单词首字母大写 print(s.count('x')) # 统计该元素个数有几个。 print(s.split(' ')) # 字符串以指定参数内的元素左右分隔成新的列表。 s1 = 'xXinXin大姐姐' print(s1.center(20,'~')) # 居中,空白填充 print(s1.startswith('xx')) # 判断字符串以什么开头 print(s1.startswith('i',2,5)) # 切片查找i开头的 print(s1.find('X')) # 通过元素找索引,找不到返回 -1 print(s1.index('X')) # 通过元素找索引,找不到会报错。 print(s1.replace('Xin','liang',2)) print(len(s1)) # 公共方法
# 应用场景:转换/t,多用于各种财务报表 str = "runoob\t12345\tabc" # 将/t转换成4个空格,括号内参数4,表示几个空格。 print(str.expandtabs(4))
# 应用场景:验证码。加入数字无影响 s_str = 'xCDvi' you_input = input('请输入验证码,不区分大小写') if s_str.upper() == you_input.upper(): print('输入成功') else: print('请重新输入')
# 应用场景:默认删除字符串前后空格, username = input('请输入名字:').strip() if username == 'xxx': print('you are beautiful') s2 = 'lsplsplsplsp' # 参数内定义元素也可删除前后元素 print(s2.strip('lp')) # 也可以指定方向,rstrip 和 lstrip .
# is系列 name = 'xxinxin688' print(name.isalnum()) # 字符串由字母或数字组成 print(name.isalpha()) # 字符串只由字母组成 print(name.isdecimal()) # 字符串只由数字组成
(4)list:存储大量数据。用中括号 [ list ] 包括。
(5)tuple:元组又叫只读列表。用小括号 ( tuple ) 包括。
(6)dict:储存关系型数据,字典有对应的键值。用于大括号 { dict } 包括。
(7)集合:也是用于大括号 { 集合 } 包括。里面也是用储存数据。